In this article, you’ll learn:
In this digital age, it's easy to create and share digital content. Everybody can download or copy original content and reuse it elsewhere – be it cat memes, bored apes GIFs, or the latest version of the Windows operating system. But it’s a big problem for creators and companies that spend a lot of time, money, and effort to make digital assets for monetary benefits.
Enterprises are often left to wonder how to securely share their digital assets and prevent piracy and misuse.
Digital rights management (DRM) solves this problem. Just like you lock your door before you go out to protect your property, you lock in your digital assets with DRM. It’s a proactive way of protecting your digital intellectual properties before theft or illegal use.
Read on to learn all about DRM: how it works, why enterprises need it, its benefits, and use cases.
What is a digital asset?
Before we delve into DRM, let’s understand what exactly constitutes “digital assets” that need to be protected.
A digital file is considered a digital asset when an individual or an organization pours considerable time, effort, and resources into its creation and when it adds business value to the company.
Your Word file with a to-do list for a marketing campaign isn’t a digital asset. But your company logo, images, and videos used in a marketing campaign definitely are. From confidential information to proprietary information, every valuable digital file is a digital asset.
Your digital assets could be:
- Software
- Photographs
- Word documents and PDFs
- Slide presentations
- Spreadsheets
- Music and other audio files
- Video, animations, illustrations
- Logos
- Books
- Games
- Websites
- Content
- Metadata
- Contracts

Digital assets like these are shared and traded back and forth within enterprises and outside the company to consumers. Not securing such file exchanges poses a risk of piracy, unauthorized use, and loss of revenue. A user may not be penalized for downloading and using a copyrighted image as their desktop saver, but for companies that put in money to create that file for commercial use, it's a revenue loss. That’s where DRM comes in.
What is digital rights management?
Technology marketplace G2 defines DRM as “a systematic method of protecting copyrighted digital media.” It safeguards, controls, and manages access to copyrighted digital assets such as software or multimedia.
You can only watch Stranger Things on Netflix when you log in to your Netflix account. Why?
Because the company protects its content from being accessed without proper authorization. The same goes for your Apple iTunes and Amazon Kindle. For any DRM-protected digital assets, a user has to prove they are entitled to use the digital material in question.
To be clear, DRM is not the copyright itself, but technology that secures the rights of the copyright holder. DRM doesn’t restrict access to free content but protects copyrighted work from being accessed or used without permission.
Digital rights management vs. digital asset management
If digital rights management is about managing access to digital assets, then what is digital asset management (DAM)?
Even though they are closely related, they aren’t the same thing. DAM is a system for businesses that organizes, stores, retrieves, and shares digital assets in a structured way. DRM, on the other hand, is about protecting valuable digital assets from piracy and copyright issues by managing and restricting access to it. When businesses are considering platforms to manage and protect these assets, it’s crucial to compare tools and services. For example, eToro compared to Trading 212 offers different approaches to managing digital assets in the context of trading and investments.
Today, many DAM software have built-in DRM. Pics.io, for instance, supports DRM methods like watermarking and terms and conditions clauses. When you're sharing assets outside of your organization with Websites, you can include T&C to specify why and how these assets can be used and distributed
For existing licences that you need to manage, there is an option to link license files and assets together so they would be always at hand's reach.
How DRM works
DRM performs four main functions:
- Prevents unauthorized access to digital assets
- Restricts which users can access and what they can do with digital assets
- Deters unauthorized use by making it difficult to copy or download files
- Detects unauthorized use, like with watermarks, pattern match, or plagiarism detection tools.
These functions are done by placing restrictions on digital content using encryptions.
- DRM software encodes a digital asset with a special computer program that gets decoded with another program or a cryptographic key.
- The key is again protected by the DRM server with a digital license containing rules on user access and usage.
- When an authorized user requests access, their user license is verified by the DRM server.
- Once authenticated, the user can access the digital content.
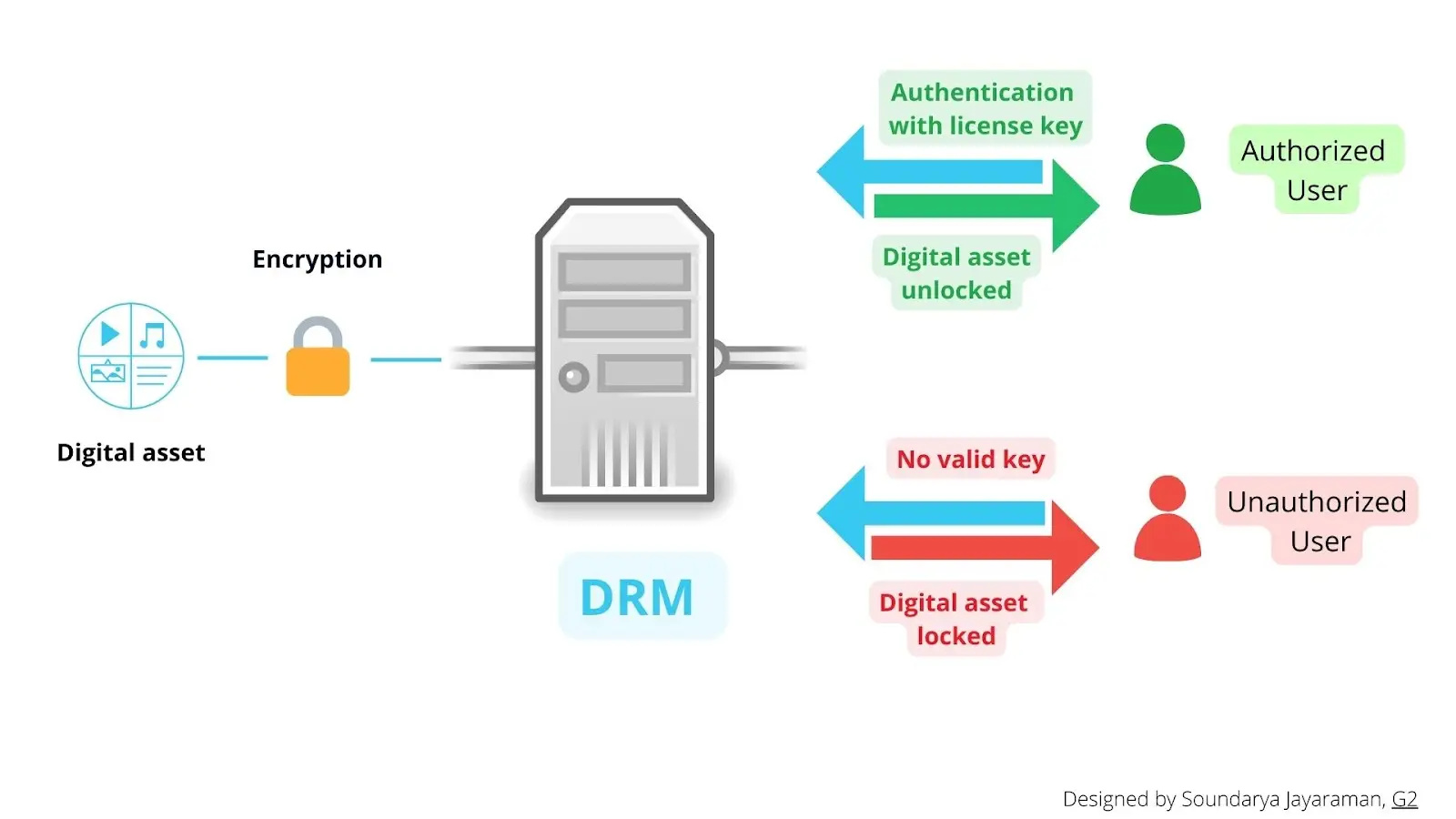
The request can be as simple as your Netflix account username and password. DRM finds your license with information about your access and usage level, decodes encryption accordingly, and delivers your video content. The most commonly used encryption standard is advanced encryption standard-128 (AES-128).
With encryption, DRM manages permission to access a digital asset in several ways, such as user authentication, IP authentication, or product authentication. For instance, many software providers give users a product key to access their applications. The user has to enter the key to run the application.
With such access control, the tools limit:
- The types of devices a user can gain access from.
- The number of devices each subscriber can use.
- The duration of access
- The level of access
They also control what users can do with the shared content. Even if you copy a DRM-protected file, you won’t be able to open it without a proper key since it's encrypted. A simple example of this would be the inability to download a Netflix show or Spotify album outside the application into your device.
Currently, DRM can be both software and hardware solutions. It can be the product key Microsoft provides for Windows or your Xbox console t.
Types of digital rights management tools
Different DRM technologies are used to achieve access control and copy protection. Explore the various DRM tools below.
Product keys
Commonly used by software providers, a product key is an alphanumeric string that user enters when installing software or product. Without the correct product key, the software won’t activate.
For example, installing Windows operating system on a laptop requires the correct product key from Microsoft to complete the process.
Always-on DRM
This is also known as persistent online authentication. Always-on DRM requires the user to be connected to the server through the internet to access the digital asset. Many online video games, like Age of Empire and Diablo III, require users to remain connected to online servers to play them.
This isn’t limited just to software. Some hardware tools also require a connection to an online server to access digital files. For instance, certain gaming consoles, like Playstation 3, 4, and 5, require an online connection to play.
Activation Limits
This DRM class limits the number of systems where the user can install software or digital assets. Somebody can use their Netflix premium subscription on a maximum of four devices and watch on all four devices at the same time. Many software-as-a-service (SaaS) providers also use this type of DRM software.
Regional lockout or coding
This DRM technology prevents access to a digital service outside a certain geographical area. Such technology tracks IP addresses and disables or enables certain software or hardware features depending on the region. For instance, sometimes when you try to watch a movie that’s not available in your country, you get a message saying:
“This video you are trying to watch cannot be viewed from your location or country.”
That’s regional lockout DRM in action.
Video streaming services, gaming consoles, smartphones, printers, tablets, computers, and even credit cards have regional lockout DRMs.
Copy Protection
This DRM system restricts illegal copying and redistribution of digital files by encryption. Both multimedia content creators and enterprises use it to prevent unauthorized copying. Tools like Microsoft PlayReady, Apple Fairplay, or Adobe DRM provide copy protection through encryption.
Software tampering
In this DRM method, digital assets or products have dormant bugs that prevent their use whenever they’re accessed illicitly. Video game creators usually place bugs to slow games or disable certain features for illegal users.
Enterprise DRM
Also called information rights management, enterprise DRM shields data across an enterprise. It used standard DRM tech: encryption coupled with a policy about access and use of digital assets by company employees and partners..
Watermark
Watermarking is an add-on to other DRM technologies. Watermarks embed a unique mark on a digital asset that’s not removable unless authorized to. There are two common types of watermarks used:
- Visible watermark - watermark visible to end user on the digital asset
- Forensic watermark - watermark embedded as an identifying code in the digital asset, invisible to the user
Such marks establish ownership and also help track any unauthorized usage.
Why your enterprise needs DRM
Every year, the US economy loses more than $300 billion from IP thefts and at least $29 billion from online piracy alone. Internet users visited piracy websites 132 billion times between January and September last year.
For people, downloading, copying, or reusing digital content or software isn’t theft or crime. After all, it harms no one. But it’s a serious business issue for companies. And when it comes to digital assets that have sensitive business information, any illegal or unauthorized use results in business loss.
Napster, the free music-sharing internet platform was sued and shut down because it caused revenue loss for music labels and creators. But this can’t happen in all cases. Pirates are everywhere and companies can’t go and apprehend every single illegal user. But they can protect their assets by controlling access using DRM.
DRM acts as the security guard at the gate, checking in and permitting only authorized users and managing them once they are inside. In this way, it protects the creative and financial investment that went into it.
Companies are using DRM along with digital asset management (DAM) to manage their brand assets and also keep track of their licenses to avoid copyright violations.
Eight benefits of digital rights management
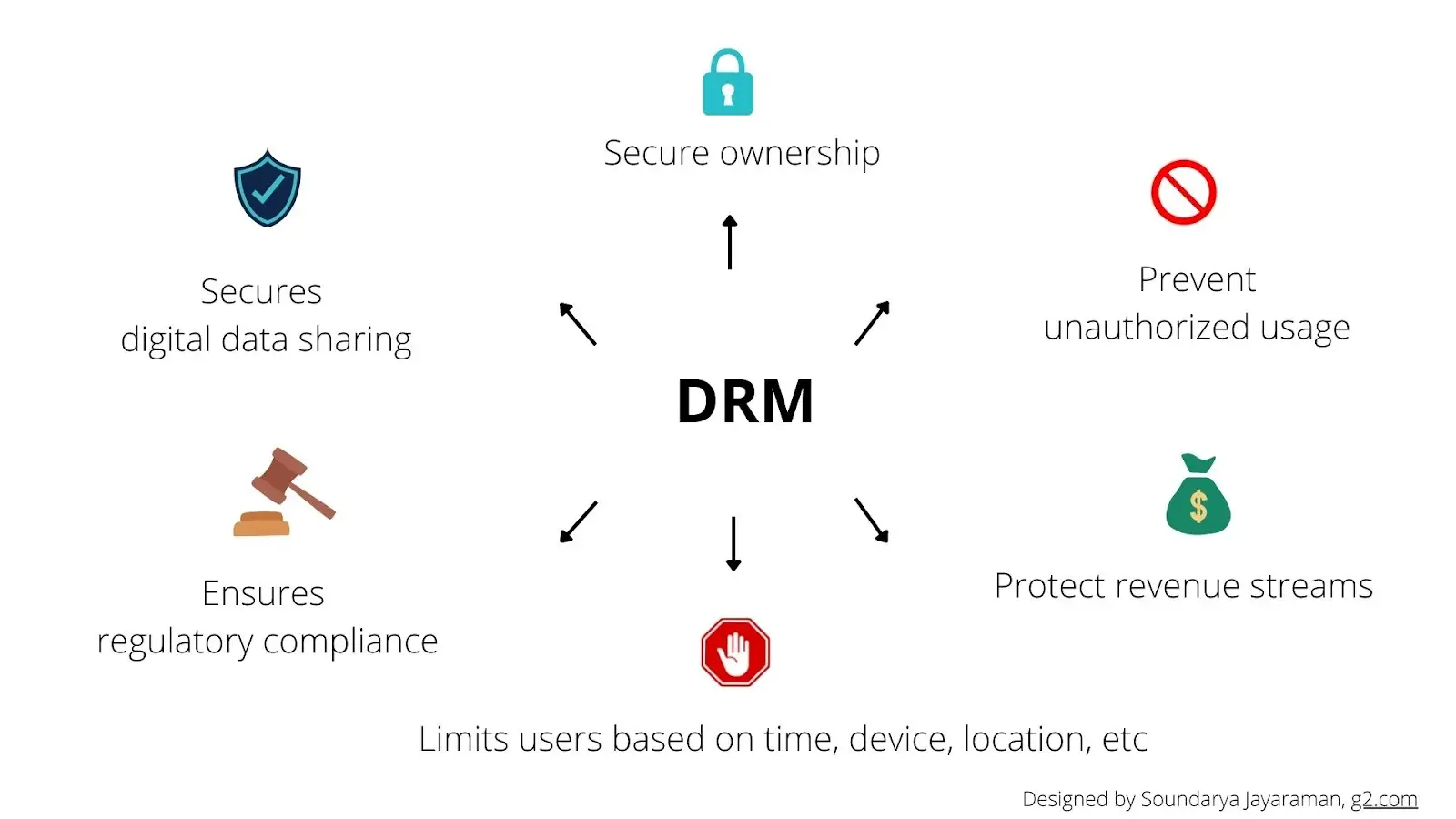
DRM benefits you and your organization by:
- Securing and retaining ownership of your digital assets by preventing any unauthorized alteration or reuse.
- Preventing unauthorized users from copying, saving, editing, or sharing your content.
- Making access and usage details transparent to users.
- Sharing confidential data securely.
- Limiting user access to a digital asset based on duration, device, or location.
- Monitoring digital asset usage.
- Safeguarding revenue streams and stopping any leaks.
- Ensuring compliance with relevant data protection laws.
DRM use cases by the industry
DRM is used to protect digital assets in any form. Some common applications of DRM tools across different industries are detailed below.
Software
Software piracy has existed since the time of the internet. 37% of software installed on personal computers is unlicensed. Unlicensed software not only costs businesses but also makes users susceptible to malware attacks. Software providers use DRM, specifically copy-protection technologies, to prevent unlicensed use of their tech.
Media & Entertainment
Digital disruption and high-speed internet have made the distribution of digital content like films, music, and videos easier. However, it’s also made piracy rampant. Television, films, and music industries remain among the top five pirated sectors. To combat this, many media content producers, media distributors, and content publishers use DRM. Subscription services like Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Disney Hotstar use DRM technology such as Apple Fairplay, Google Widevine, and Microsoft PlayReady. Live streaming services also use DRM to prevent stream ripping. A SRT streaming server can also ensure secure and reliable live video delivery.
Gaming industry
Another industry prone to piracy, gaming companies now use DRM to authenticate a user’s purchase. Major game distributors like Steam, publishers like Ubisoft and Activision-Blizzard, and console manufacturers like Nintendo, Sony, and Microsoft use DRM in their products.
Book Publishers
Publishers lose more than $300 million every year to ebook piracy. It’s the second-largest pirated industry with 30 billion visits to piracy websites recorded in just nine months of 2021. Many publishers use DRM tools to make their books accessible only to legitimate customers.
Publishers can design their own Ebook DRM in-house or purchase it from a vendor. Amazon and Apple, for instance, have their own in-house DRM for all ebooks. Barnes & Noble, Kobo, and Google, on the other hand, use Adobe DRM.
Enterprise
Businesses are increasingly using enterprise DRM to manage sensitive digital assets – from Word documents to internal or external emails. Managers and IT administrators decide who can access which digital asset and how they can use it. Additionally, companies utilize DRM along with DAM to manage their brand’s digital marketing assets. This goes a long way in maintaining brand consistency across platforms.
Digital marketing agencies
Digital marketing and content creation agencies use DRM to manage their clients' digital assets. From ideation and creating to licensing and distributing the digital assets of a client, DRM provides easy access as well as protection.
In addition to these applications, DRM tools are also used in healthcare, education, research, and investment to store, manage and share confidential data.
Features of digital rights management tool
An all-encompassing DRM tool should have the following features:
- Support for various digital asset formats like text, video, image, audio, or slides
- User identity and access management
- Copy protection
- Access control according to set limits based on user, duration, location, device, or IP address
- Support for all devices, operating systems, file management systems, and other applications
- Interoperable with industry solutions such as Apple Fairplay and Google Widevines
- Analytics on asset access and usage
Today, there are many SaaS providers as well as big tech companies that offer DRM solutions. The solutions differ based on:
- Type of asset to be protected.
- Level of protection.
- Intended audience or user.
- Cloud-hosted or on-premise solutions.
- Tech support and scalability.
Based on your needs and budget, you can select the right DRM solution from the market.
Protect yourself
If your company wants to protect your digital assets and doesn't want to lose millions, DRM is the answer. Identify the digital assets you want to protect. Research your users and choose a DRM solution that is flexible. Make sure your DRM tool doesn’t hinder your user experience.
Implement DRM and protect you and your company.
Curious? Learn more about Pics.io or book a demo with us and we'll answer all of your questions!
Author

Soundarya Jayaraman is a content community writer at G2.com. She loves to learn and write about the latest technologies and how they can help businesses. When she is not writing, you can find her painting or reading. LinkedIn | Twitter



