Contents:
An image CDN (Content Delivery Network) is like a worldwide delivery system for your visuals. Instead of loading images from a single server, it stores them on multiple servers across the globe—so when someone visits your site, they get the images from the nearest location. Faster load times, smoother user experience, no matter where your audience is. And on top of that, an image CDN automatically adjusts and optimizes each image to match the user’s device and connection speed. Simply put, your pages load faster, and your images always look their best.
At Pics.io, we’ve had some basic CDN-like features tucked into our DAM for a while—because our users needed them. But over time, we started hearing the same request more and more clearly: “Can you make this bigger? Can you make it a real CDN?” So we did.
The interesting part? Teams that use both DAM and CDN typically have to buy them separately. It’s just how the market works. CDNs are usually treated as stand-alone tools, and almost no one searches for a DAM system that includes one. Even our marketing team struggled to find keywords to promote this combo—because people didn’t think it existed.
But now it does.
We’ve built a fully functional image CDN right into Pics.io as an optional add-on. Not just a checkbox or a helper tool—a real CDN designed with visuals in mind.
Why focus on images? Because that’s what our users share most—product photos, event galleries, service portfolios, social content. Of course, CDNs can technically deliver other file types too—videos, PDFs, etc. And if we see the demand, we’ll go there. But right now, this one’s for your images.
So here’s the big news: Pics.io users can now get a full-featured image CDN as part of their DAM toolkit. Let’s talk about what that means—and how it works.
What a CDN Can Do: Key Performance Stats in One Table
| Metric | With a Fast CDN | Without a CDN or Slow Load | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Page Load Time | 1 second | 5 seconds | Users are 3× more likely to convert |
| Conversion Rate | ~3.0% | ~1.0% | Every second saved = +4.4% conversions |
| Bounce Rate | 7% | 38% | Lower bounce keeps users engaged |
| Mobile Bounce (at 10s load) | — | 123% higher | Fast mobile load is critical |
| Returning Visitors | More likely | 10% drop per extra second | Speed builds loyalty |
| Origin Server Load | Reduced | High during traffic spikes | More stability & cost savings |
| Tail Latency (worst-case delay) | Up to 67% lower | Slower, inconsistent | Better performance for all users |
What Is a CDN and Why It Matters
Let’s start with the basics—what is a CDN?
A CDN, or Content Delivery Network, is a geographically distributed group of servers that work together to deliver web content faster. Instead of relying on a single server to send data to users everywhere, a CDN caches that data in multiple locations around the world. This way, users load content from the server that's physically closest to them, resulting in a much faster and more reliable experience.
In other words, a CDN takes the weight off your origin server and brings content closer to the people who actually need it.
Behind the Scenes: How a CDN Works
Imagine a network of “edge servers” placed across the globe. These servers—often called Points of Presence (PoPs)—are where your content is stored and served from. When someone visits your site, their request doesn’t have to travel all the way to your central server. Instead, DNS and Anycast routing quickly direct the request to the nearest PoP, which responds with cached content.
There are two common caching models:
- Pull: Content is fetched from your origin when first requested and then cached.
- Push: You manually upload content to the CDN in advance.
The CDN can also optimize what it delivers—resizing images, compressing files, and even adjusting content based on the device or connection speed.
Why Use a CDN: The Key Benefits
What is the role of a CDN in web performance? That’s exactly where CDNs prove their value—and not just for big enterprises or streaming giants. Today, speed isn't a nice-to-have. It's a deal-breaker. Whether you're running an e-commerce store, a media platform, or a SaaS dashboard, a CDN gives you the performance edge.
Let’s break it down:
- Speed That Actually Moves the Needle
The closer your content is to your user, the faster it loads. A CDN stores cached versions of your content on servers located all around the world. So instead of waiting for data to travel halfway across the globe, your users get what they need from a nearby location—fast.
This reduces latency, accelerates page load times, and creates a smoother experience across devices and networks. Users stay longer, click more, bounce less.
- Lower Bounce, Higher Conversion
Speed isn’t just about satisfaction—it directly affects your bottom line. A page that loads in one second can convert visitors at more than double the rate of a five-second load. And the longer it takes, the higher the bounce rate. A CDN can help you shave off those precious seconds and keep users engaged from the first click.
- Lighter Load on Your Servers
When content is served from edge locations, your main (origin) server isn’t overwhelmed by every single request. That means fewer slowdowns, fewer crashes, and less need for expensive server scaling. You save money on bandwidth, and your infrastructure becomes much more resilient—especially during peak hours, product launches, or viral traffic spikes.
- Built-in Protection
CDNs do more than speed things up—they add a solid layer of defense. Most CDNs come equipped with:
- DDoS attack mitigation
- Web Application Firewalls (WAF)
- SSL/TLS encryption for secure data transfer
They can absorb malicious traffic, filter out harmful requests, and keep your core systems safe—without making you lift a finger.
- SEO + User Experience
Google has made it clear: site speed impacts rankings. Faster sites not only earn better spots in search results but also perform better across Core Web Vitals metrics. A good CDN helps you meet those standards, offering:
- Faster loading
- Reduced layout shifts
- Better interaction timing
The result? Better SEO, better visibility, and a better chance of turning visitors into customers.
- Scales As You Grow
One of the underrated benefits of a CDN is how well it scales. Whether you're serving 1,000 users a day or 1 million, performance stays consistent. You don’t need to worry about provisioning extra infrastructure or upgrading your hosting plan every time traffic spikes. The CDN takes the hit for you.
When a CDN Isn’t Perfect: Limitations and Risks
Still, no tool is perfect.
One challenge is that CDNs work best with static content. Dynamic, real-time data doesn’t cache easily and may still require direct server calls.
Another concern? Complexity. Setting up and configuring a CDN—especially one with advanced features—can be intimidating for small or non-technical teams. Add costs, and some businesses hesitate.
There are also risks tied to control and regulation. GDPR compliance can get tricky, and central failures—like the 2021 Fastly outage—show how dependent we become on these networks.
Sometimes, a CDN simply isn’t necessary. If your audience is local, your traffic is low, and your hosting is already fast, the added layer might not bring significant benefits.
Real-World Use Cases for a CDN
| Use Case | What a CDN Content Delivery Network Helps With |
|---|---|
| E-commerce | Faster product images, localized catalogs, and quick cart updates |
| Media & Streaming | Smooth video playback, even in high resolution |
| Corporate & SaaS Sites | Better uptime, improved load speeds, and higher conversions |
| APIs and Microservices | More responsive systems, especially under load |
How to Set Up a CDN: A Step-by-Step Guide
Let’s break down what CDN is and how it works—in practical steps.
- Understand your needs: Where is your audience? What types of content are slowing you down?
- Choose the right CDN: Public, private, or even multi-CDN setups depending on your goals.
- Configure your DNS and SSL: This links your domain with the CDN and ensures secure delivery.
- Set caching rules: Define what’s cached, for how long, and when it refreshes.
- Monitor and optimize: Use analytics to track performance, spot bottlenecks, and improve delivery.
FAQ: Everything You Wanted to Ask About CDNs
What does CDN stand for?
CDN stands for Content Delivery Network—a system of globally distributed servers that work together to deliver digital content (like images, videos, and webpages) faster by caching it closer to the user.
How is a CDN different from regular hosting?
Web hosting stores your files in one place—usually a single server or data center. A CDN, on the other hand, delivers cached copies of your content from multiple locations worldwide. This reduces the distance between the server and the user, speeding up delivery and improving reliability.
Does every website need a CDN?
Not necessarily. If your site has low traffic, serves a local audience, or already loads very fast, the difference may be minimal. But if your users are global, or your site contains heavy visual content, a CDN can make a noticeable difference in speed, SEO, and user experience.
Is setting up a CDN difficult?
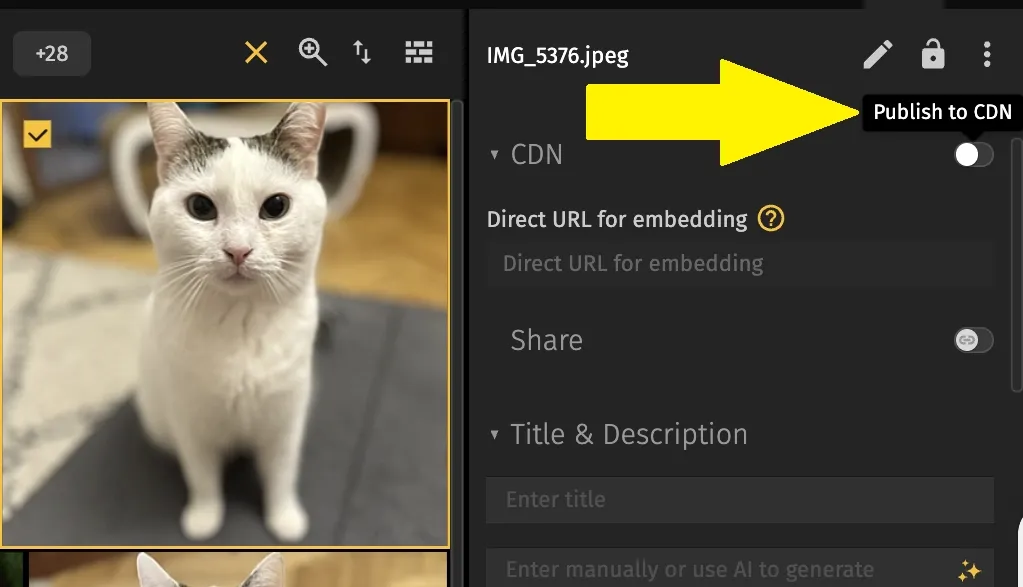
It depends on the tool. Some CDN setups can be technical and time-consuming. But if you use a platform like Pics.io, the process is simple. Just enable CDN delivery in your settings, and you’re good to go—no advanced setup or coding required.
Can a CDN help with SEO?
Yes. Faster websites tend to rank higher on Google. A CDN improves Core Web Vitals like load time and interaction speed, which are now key factors in SEO performance.
Is a CDN secure?
Most modern CDNs include built-in security features like SSL/TLS encryption, DDoS protection, and Web Application Firewalls (WAF). These help protect your site and users from common online threats.
Can a CDN deliver more than just images?
Definitely. While image delivery is a common use case, CDNs can also handle videos, HTML/CSS/JS files, fonts, documents, and even API responses. That said, our CDN in Pics.io is currently focused on optimized image delivery—where speed matters most.
Did you enjoy this article? Give Pics.io a try — or book a demo with us, and we'll be happy to answer any of your questions.
Author
Eugene PristupaAs a product manager, Eugene brings a unique blend of experience in sales, logistics, and customer support—all within the DAM space. He holds a Master’s degree in International Economics and also has skills in frontend development and analytics. Eugene has an in-depth understanding of DAM like no one else.




